TRAVEL TO SPACE
(STARS AND CONSTELLATION)
So do you want to travel space ?
Space is a difficult thing to travel because it is dangerous in space and you dont know what to expect
Some people are worthy to go through space. there called ASTRONAUT.
What is an Astronaut?
An astronaut or cosmonaut is a person trained by a human spaceflight program to command, pilot, or serve as a crew member of a spacecraft.
Some scientist made a device that can see farther things and the purpose of that device is to see stars and more..
Many kids want to be an astronaut when they grow up . To see the stars,planets,many more
But space is dangerous .......
People say that there still unidentified beings out there .And they dont know if it is friendly or Dangerous enough to kill a human being.
ALIENS
is life that occurs outside of Earth and that probably did not originate from Earth. These hypothetical life forms may range from simple prokaryotes to beings with civilizations far more advanced than humanity.
But aliens is just a myth so dont be scared XD
Stars
A star is type of astronomical object consisting of a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun.
Stars are giant, luminous spheres of plasma. There are billions of them — including our own sun — in the Milky Way Galaxy. And there are billions of galaxies in the universe. So far, we have learned that hundreds also have planets orbiting them.
Star naming
Ancient cultures saw patterns in the heavens that resembled people, animals or common objects — constellations that came to represent figures from myth, such as Orion the Hunter, a hero in Greek mythology. Astronomers now often use constellations in the naming of stars. The International Astronomical Union, the world authority for assigning names to celestial objects, officially recognizes 88 constellations. Usually, the brightest star in a constellation has "alpha," the first letter of the Greek alphabet, as part of its scientific name. The second brightest star in a constellation is typically designated "beta," the third brightest "gamma," and so on until all the Greek letters are used, after which numerical designations follow.
Star formation
A star develops from a giant, slowly rotating cloud that is made up entirely or almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. Due to its own gravitational pull, the cloud behind to collapse inward, and as it shrinks, it spins more and more quickly, with the outer parts becoming a disk while the innermost parts become a roughly spherical clump. According to NASA, this collapsing material grows hotter and denser, forming a ball-shaped protostar. When the heat and pressure in the protostar reaches about 1.8 million degrees Fahrenheit (1 million degrees Celsius), atomic nuclei that normally repel each other start fusing together, and the star ignites. Nuclear fusion converts a small amount of the mass of these atoms into extraordinary amounts of energy — for instance, 1 gram of mass converted entirely to energy would be equal to an explosion of roughly 22,000 tons of TNT.
Characteristics of stars
Brightness
Astronomers describe star brightness in terms of magnitude and luminosity.
The magnitude of a star is based on a scale more than 2,000 years old, devised by Greek astronomer Hipparchus around 125 BC. He numbered groups of stars based on their brightness as seen from Earth — the brightest ones were called first magnitude stars, the next brightest were second magnitude, and so on up to sixth magnitude, the faintest visible ones. Nowadays astronomers refer to a star's brightness as viewed from Earth as its apparent magnitude, but since the distance between Earth and the star can affect the light one sees from it, they now also describe the actual brightness of a star using the term absolute magnitude, which is defined by what its apparent magnitude would be if it were 10 parsecs or 32.6 light years from Earth. The magnitude scale now runs to more than six and less than one, even descending into negative numbers — the brightest star in the night sky is Sirius, with an apparent magnitude of -1.46.
Luminosity is the power of a star — the rate at which it emits energy. Although power is generally measured in watts — for instance, the sun's luminosity is 400 trillion trillion watts— the luminosity of a star is usually measured in terms of the luminosity of the sun. For example, Alpha Centauri A is about 1.3 times as luminous as the sun. To figure out luminosity from absolute magnitude, one must calculate that a difference of five on the absolute magnitude scale is equivalent to a factor of 100 on the luminosity scale — for instance, a star with an absolute magnitude of 1 is 100 times as luminous as a star with an absolute magnitude of 6.
The brightness of a star depends on its surface temperature and size.
Color
Stars come in a range of colors, from reddish to yellowish to blue. The color of a star depends on surface temperature.
A star might appear to have a single color, but actually emits a broad spectrum of colors, potentially including everything from radio waves and infrared rays to ultraviolet beams and gamma rays. Different elements or compounds absorb and emit different colors or wavelengths of light, and by studying a star's spectrum, one can divine what its composition might be.
Surface temperature
Astronomers measure star temperatures in a unit known as the kelvin, with a temperature of zero K ("absolute zero") equaling minus 273.15 degrees C, or minus 459.67 degrees F. A dark red star has a surface temperature of about 2,500 K (2,225 C and 4,040 F); a bright red star, about 3,500 K (3,225 C and 5,840 F); the sun and other yellow stars, about 5,500 K (5,225 C and 9,440 F); a blue star, about 10,000 K (9,725 C and 17,540 F) to 50,000 K (49,725 C and 89,540 F).
The surface temperature of a star depends in part on its mass and affects its brightness and color. Specifically, the luminosity of a star is proportional to temperature to the fourth power. For instance, if two stars are the same size but one is twice as hot as the other in kelvin, the former would be 16 times as luminous as the latter.
Size
Astronomers generally measure the size of stars in terms of the radius of our sun. For instance, Alpha Centauri A has a radius of 1.05 solar radii (the plural of radius). Stars range in size from neutron stars, which can be only 12 miles (20 kilometers) wide, to supergiants roughly 1,000 times the diameter of the sun.
The size of a star affects its brightness. Specifically, luminosity is proportional to radius squared. For instance, if two stars had the same temperature, if one star was twice as wide as the other one, the former would be four times as bright as the latter.
Mass
Astronomers represent the mass of a star in terms of the solar mass, the mass of our sun. For instance, Alpha Centauri A is 1.08 solar masses.
Stars with similar masses might not be similar in size because they have different densities. For instance, Sirius B is roughly the same mass as the sun, but is 90,000 times as dense, and so is only a fiftieth its diameter.
The mass of a star affects surface temperature.
Magnetic field
Stars are spinning balls of roiling, electrically charged gas, and thus typically generate magnetic fields. When it comes to the sun, researchers have discovered its magnetic field can become highly concentrated in small areas, creating features ranging from sunspots to spectacular eruptions known as flares and coronal mass ejections. A recent survey at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics found that the average stellar magnetic field increaseswith the star's rate of rotation and decreases as the star ages.
Metallicity
The metallicity of a star measures the amount of "metals" it has — that is, any element heavier than helium.
Three generations of stars may exist based on metallicity. Astronomers have not yet discovered any of what should be the oldest generation, Population III stars born in a universe without "metals." When these stars died, they released heavy elements into the cosmos, which Population II stars incorporated relatively small amounts of. When a number of these died, they released more heavy elements, and the youngest Population I stars like our sun contain the largest amounts of heavy elements.
Star classification
Stars are typically classified by their spectrum in what is known as the Morgan-Keenan or MK system. There are eight spectral classes, each analogous to a range of surface temperatures — from the hottest to the coldest, these are O, B, A, F, G, K, M and L. Each spectral class also consists of 10 spectral types, ranging from the numeral 0 for the hottest to the numeral 9 for the coldest.
Stars are also classified by their luminosity under the Morgan-Keenan system. The largest and brightest classes of stars have the lowest numbers, given in Roman numerals — Ia is a bright supergiant; Ib, a supergiant; II, a bright giant; III, a giant; IV, a subgiant; and V, a main sequence or dwarf.
A complete MK designation includes both spectral type and luminosity class — for instance, the sun is a G2V.
Stellar structure
The structure of a star can often be thought of as a series of thin nested shells, somewhat like an onion.
A star during most of its life is a main-sequence star, which consists of a core, radiative and convective zones, a photosphere, a chromosphere and a corona. The core is where all the nuclear fusion takes places to power a star. In the radiative zone, energy from these reactions is transported outward by radiation, like heat from a light bulb, while in the convective zone, energy is transported by the roiling hot gases, like hot air from a hairdryer. Massive stars that are more than several times the mass of the sun are convective in their cores and radiative in their outer layers, while stars comparable to the sun or less in mass are radiative in their cores and convective in their outer layers. Intermediate-mass stars of spectral type A may be radiative throughout.
After those zones comes the part of the star that radiates visible light, the photosphere, which is often referred to as the surface of the star. After that is the chromosphere, a layer that looks reddish because of all the hydrogen found there. Finally, the outermost part of a star's atmosphere is the corona, which if super-hot might be linked with convection in the outer layers.
But the good thing in space is theres no gravity you can jump whatever you want .And thats not it ,
you can see planets and stars .when you are in the ground sitting and watching the stars ,it is beautiful
because they are shiny and they sparkle sometimes.they formed shapes and it is beautiful to watch the sky pitch black with perfectly balanced stars .It is a great combination of Dark and Light.
there are many kinds of stars and different shapes and sizes.you cant count how many stars are there the best part if you go to space is the view of the earth . you can see the clouds ,and you can see how tiny is the earth compare to the other planets
The best view you can see from earth is the constellations
they form different shapes and there is a name of that constellations .
constellation
is a group of stars forming a recognizable pattern that is traditionally named after its apparent form or identified with a mythological figure. Modern astronomers divide the sky into eighty-eight constellations with defined boundaries.
20 Facts About Constellations
1. The word “constellation” comes from a Latin term meaning “set with stars.”
2. Farmers were the first to use the constellations. In some areas the changing of seasons was so subtle that the farmers depended on the stars to know when it was time to plant and when the time was right to harvest.
3. Astronomers have divided the sky into 88 different constellations.
4. We know the constellations have been around for centuries, historical records in 4000 B.C. (Mesopotamian culture) refer to these bodies of stars. Homer’s epic poem, the Odyssey talks about the constellations and Eudoxus of Cnidus wrote about 43 constellations, 400 years later.
5. A book written in 150 A.D. called, Almagest, was written by an Alexandrian astronomer, Ptolemy. He used historical data provided at the time from 120-150 A.D. He claims to have taken data from as far back as the 8th century B.C. Babylonia.
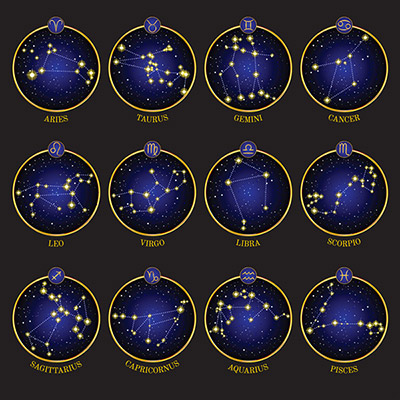
The Zodiac Constellations
6. The stars are broken up into groups. The 21 Northern Constellations are; Andromeda, Aquila, Auriga, Boötes, Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Corona Borealis, Cygnus, Delphinus, Draco, Equuleus, Hercules, Lyra, Ophiuchus, Pegasus, Perseus, Sagitta, Serpens, Triangulum, Ursa Major and Ursa Minor.
7. There are 15 Southern Constellations; Ara, Argo Navis, Canis Major, Canis Minor, Centaurus, Cetus, Corona Australis, Corvus, Crater, Eridanus, Hydra, Lepus, Lupus, Orion and Pisces Austrinus.
8. Astrology also has their own set of 12 Zodiacal Constellations; Aries, Aquarius, Cancer, Capricornus, Gemini, Leo, Libra, Pisces, Sagittarius, Scorpius, Taurus and Virgo.
9. These original constellations were the only ones to be named until a German Globe maker named, Casper Vopel added two more in 1536. They are called; Coma Berenices and Antinous.
10. In Ancient Greek they did not name any constellations with the southern stars until 1589, when a Dutch astronomer named, Plancius began to fill the southern celestial void. He created, Crux and Triangulus Antarcticus. From here he went on to create many more constellations.
11. The Greeks are responsible for naming the constellations. These names came from their mythological heroes and legends.
12. Before fancy navigational equipment on seafaring ships, the stars were used to pinpoint their locations; Polaris (The North Star) and Ursa Minor (Little Dipper constellation) were used to figure out latitude (North/South) by how high Polaris was in the sky.
Polaris
13. In the Hindu culture, the Nakshatra is the term for lunar mansion. A nakshatra is one of 27 (sometimes also 28) sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to the most prominent patterns of stars in the respective sectors.
14. Each constellation has Greek mythology and stories about how they came to be. These stories usually involve angry gods and mysterious beings.
15. Today, the stars have been mapped and show their positions. However, the stars found in each constellation may not be close to each other at all. Some of the stars will shine brighter if they are closer to Earth or if they are very large stars.
16. Not everyone can see all the constellations – it depends on where you are in the world. In addition, the season of the year also plays a role in what constellations can be seen.
17. Hydra is the largest constellation by area which takes up 3.16% of the sky.
18. The smallest constellation is Crux. It only takes up 0.17 percent of the sky.
19. The Big and Little Dipper are considered asterisms. This is when a small pattern of stars is found within a constellation.
20. Twenty two different constellation names start with the letter “C”.
List of constellation :
- orion - aquila
-scorpius - bootes
- ursa major - Auriga
-canis major - Eridanus
-capricornus - delphinus
-cassiopeia - centaurus
- ursa minor - sagitta
- draco - corona borealis
-cygnus - canis minor
-lyra -crux
-lepus -triangulum
-serpens -coma berenices
-puppis -cepheus
-lupus -vulpecula
-equuleus - camelopardalis
- leo minor -corona australis
- monoceros -lacerta
-musca -horologium
-canes venatici -corvus
-octans -piscis austrinus
-hydrus -circinus
-fomax -triangulum australe
-pavo -Scutum
-tucana -pyxis
-sextans -apus
-pictor
and many more......
there are many constellation on that list .some of them have amazing shapes and others has few and common like shapes like square,triangle,rectangle..
but one constellation is so common in here that i can see it every night in the sky.
So....
So if you want to go to space as your vacation you might prepare some medical supplies and oxygen tank to breath on.its not easy to go to space because there no one to guard you but yourself .if you die out there in space your body will float until it becomes a meteor .just joking XD
astronaut has a gear on to avoid losing oxygen and that gear save you . many people are confuse that why are the astronaut sa stand on the moon because of the gravity and i think also the gear.
travelling to space is a hard thing to do . so next time you plan a vacation trip pick a safe location so that no one will get hurt.its easy to plan a vacation ,just go to the beach or different places (not in space)
But if like to go to space,you need to have a professional to guide you on your trip with your family.
its your choice , and if you do succeed or have a safe trip in space your eyes will melt because of the beautiful view you seen.space has a different and amazing view that few humans can see it.But today
everyone can see it now because of the technology,you can see space without going top space .they record what is in the space .
Thank you for reading this blog and sorry for the wrong grammar and sometimes false statements or not
thank you for the time .






